Call 1-631-753-8390 or Contact Us - We're Happy to Help!
Please choose a body region on the right for you to pin point the problem area of your body.

Shop by Condition

Shop by Brand
Understanding the nuances of blood pressure readings is essential for maintaining heart health and preventing cardiovascular diseases. Among the key concepts to grasp lies the systolic vs. diastolic blood pressure, two critical components measured during reading. This article discusses the significance of these measurements, their roles in the cardiovascular system, and the implications of their values on your health.
Blood pressure is the force that circulating blood exerts against the walls of the arteries. This measurement is crucial because it indicates the amount of work your heart must do to pump blood throughout your body and the resistance it encounters in the arteries. Healthy blood pressure ensures that your body receives adequate blood supply to function properly without overburdening the heart and blood vessels.
Understanding Systolic Blood Pressure
Systolic blood pressure, the top number in a blood pressure reading, measures the pressure in your arteries while your heart is beating. It reflects the force at which the heart pumps blood around the body. A normal systolic reading is below 120 millimeters of mercury (mmHg). Readings above this threshold may indicate hypertension or high blood pressure, which can increase the risk of heart disease and stroke. Systolic blood pressure is particularly important as an indicator of cardiovascular risk in older adults, as it tends to rise with age due to the stiffening of the arteries.
The Role of Diastolic Blood Pressure
Diastolic blood pressure, on the other hand, is the bottom number and measures the pressure in your arteries when your heart is resting between beats. This phase, known as diastole, allows the heart to refill with blood. A normal diastolic reading is below 80 mmHg. Elevated diastolic pressure can indicate the heart and arteries are under constant stress, even when the body is at rest, which can lead to cardiovascular complications over time.
Differences and Their Significance
The primary difference between systolic and diastolic blood pressure lies in their respective phases of the cardiac cycle. While systolic pressure provides insight into the heart's pumping efficiency, diastolic pressure reveals the condition of the arteries and how well they can maintain pressure and supply blood when the heart is not beating. Both numbers are critical for diagnosing hypertension and assessing cardiovascular risk, but they may be prioritized differently depending on the individual's age, health status, and risk factors for heart disease.
Implications of High and Low Readings
High systolic or diastolic pressure can signal hypertension, a major risk factor for heart disease, stroke, and kidney problems. Conversely, low readings might indicate hypotension, which can cause dizziness and fainting and, in severe cases, lead to inadequate blood flow to the organs. Understanding these implications is vital for early intervention and managing potential health risks.
Improving Accuracy in Blood Pressure Readings
Accurate blood pressure readings are essential for proper diagnosis and treatment. Factors such as stress, physical activity, and even the time of day can influence your readings. For the most reliable measurement, it is recommended to rest quietly for a few minutes before taking a reading, ensure you are seated comfortably with your arm at heart level, and avoid caffeine or exercise shortly beforehand.
Knowing the difference between systolic and diastolic blood pressure is crucial for understanding your cardiovascular health. These measurements provide valuable insights into the heart's functioning and the condition of your blood vessels, helping you and your healthcare provider make informed decisions about your health. Remember, maintaining a healthy blood pressure is key to preventing heart disease and ensuring your body's systems receive the oxygen-rich blood they need to function optimally.
| |
|---|
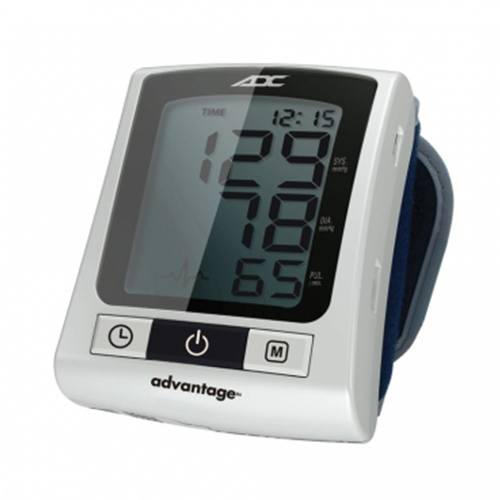 Advantage 6015N Wrist Digital Blood Pressure Monitor |
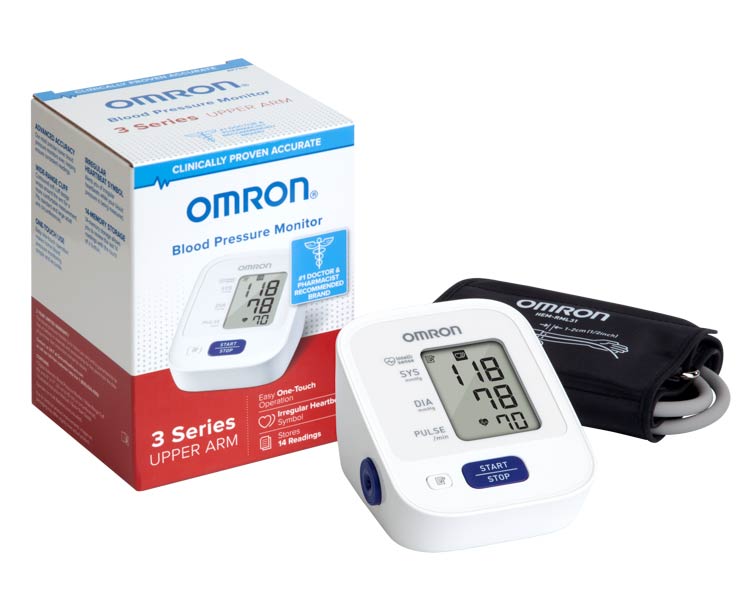 Omron 3 Series Upper Arm Digital Blood Pressure Monitor |
| |
|---|
 Adscope 601 Cardiology Stethoscope |
 Jumper Fingertip Pulse Oximeter |
 Zoll AED Plus Defibrillator with Kit |
| Stay Connected! | |
|
|
|
Related Articles
Get $10 off your next order when you sign up to receive our email newsletter.*
Simply enter your email address below!
*Minimum order value of $100. Valid email address to qualify.